AC/DC Power
Electrical power equipment for telecommunications. Part 2
Next we will go into the general operation of electrical power equipment for telecommunications.
This refers to the most commonly used backup equipment such as the generator set and batteries to keep the telecommunications infrastructure in operation.
With it, AC and DC power supply is ensured in case of commercial power failure.
For a better understanding of this content, we suggest you read the article Electrical power equipment for telecommunications. Part 1.
Generator set
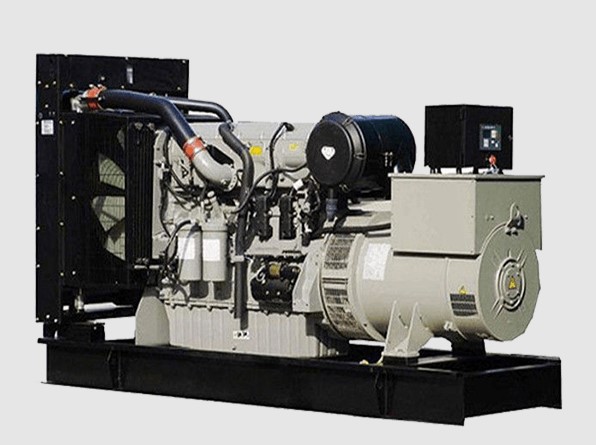

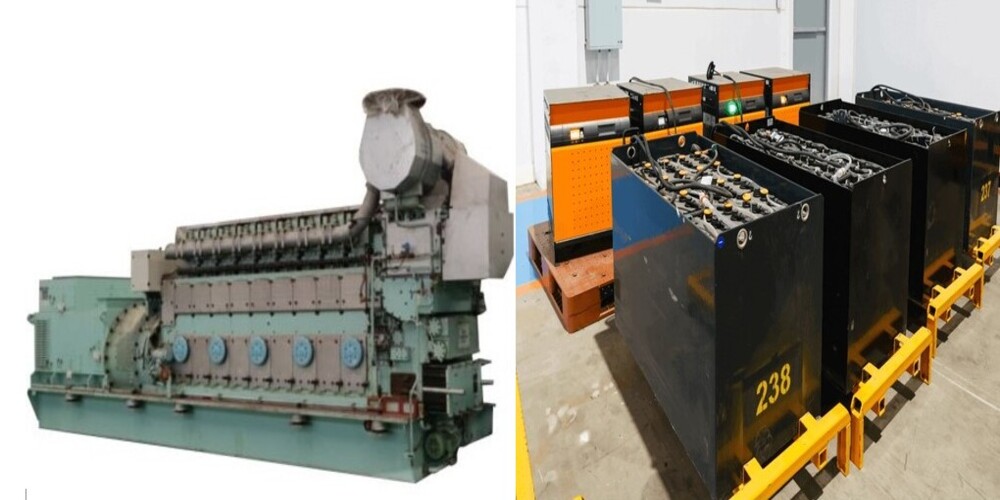
Also known as motogenerator or power plant, it is very important in telecommunication power system.
Depending on its fuel reserve, it can provide autonomy for hours or even days in case of commercial AC power failure.
It consists of a diesel engine which has an alternating current generator coupled to its shaft, which rotates at a speed suitable for producing AC power.
This equipment supplies the energy necessary to feed the critical equipment that maintains the telecommunications service. To do so, it feeds the emergency or backup AC main panel.
You should know that the calculation of the capacity of the motor-generator set depends on several factors.
In the course Sizing and selection of generator sets for telecommunications we will show you the calculation procedure to choose the most suitable from the technical-economic point of view.
On the other hand, it will allow you to know the characteristics and types of the most relevant elements of the generator sets. Finally, it includes a project of selection of this equipment so that you can clarify any doubt.
ATS or Automatic Transfer Switch
It is part of this system and it controls the engine ignition, verifies that it is working properly, detects faults in the system and others.
Depending on the active AC source, it takes one or another position, having priority to the commercial AC power supply in normal conditions.
This form of operation is represented in the following diagram, where the red lines indicate the AC energizing route to the normal and emergency service boards.
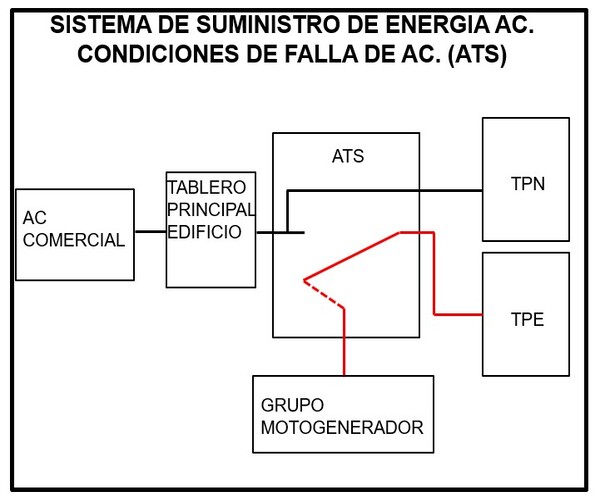
The above mentioned ATS is the one that detects any failure in the AC network such as abnormal voltage or frequency values and gives the start signal to the genset.
Under these conditions, the system is energized with AC power from the emergency services panel as follows.
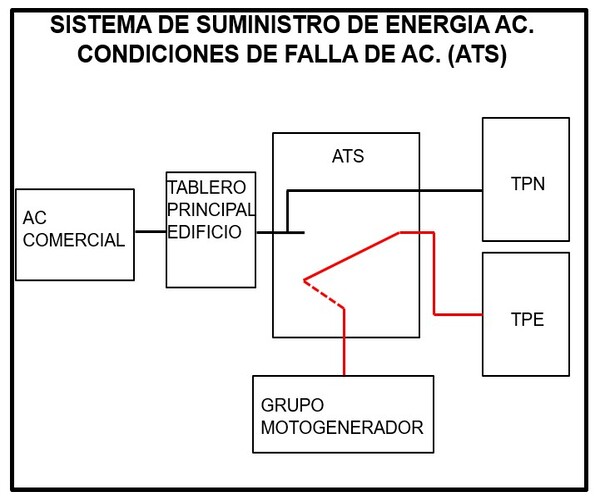
This keeps the telecommunications structure electrically operational. The time it takes to do this load transfer is about 20 to 30 seconds depending on the settings.
Due to the costs involved in its maintenance and operation, the ATS is usually given a time delay so that it emits the power-on signal in a timed manner.
This delay is about 30 seconds and ensures that the motor-generator does not turn on during very short AC power failures.
This reduces wear and tear, maintenance requirements and fuel consumption, ensuring a longer service life of this electrical energy equipment.
In our next post called Generators in telecommunications, which is still under preparation, we will be expanding on this interesting topic.
Industrial backup batteries
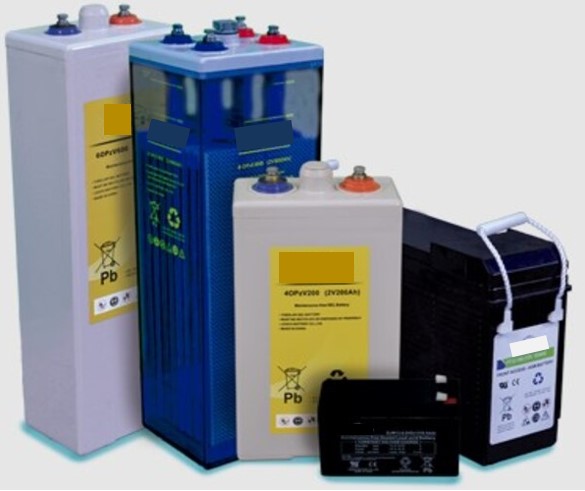

As we have already told you, the generator set can take between 20 and 30 seconds to supply the loads with AC power, starting from the moment the ATS detects the fault.
However, the telecommunications equipment cannot be left without DC power at any time, which is solved by the battery banks, which are connected in parallel with the load in the rectifier panel.
Therefore, it can be said that this electrical power equipment is the first element that provides autonomy to the telecommunications in case of failure of the AC of the commercial network.
You should know that batteries, in the telecommunication power system, have the capacity to supply DC electrical power to the loads for several hours, however, this depends on several parameters such as their capacity.
This backup time is taken into account in case of generator failure. Likewise, in locations where there is no backup power equipment, so that loads are not left without DC electricity.
Its emergency operation mode, that is, when there is no AC power and no generator set is available, can be seen below.
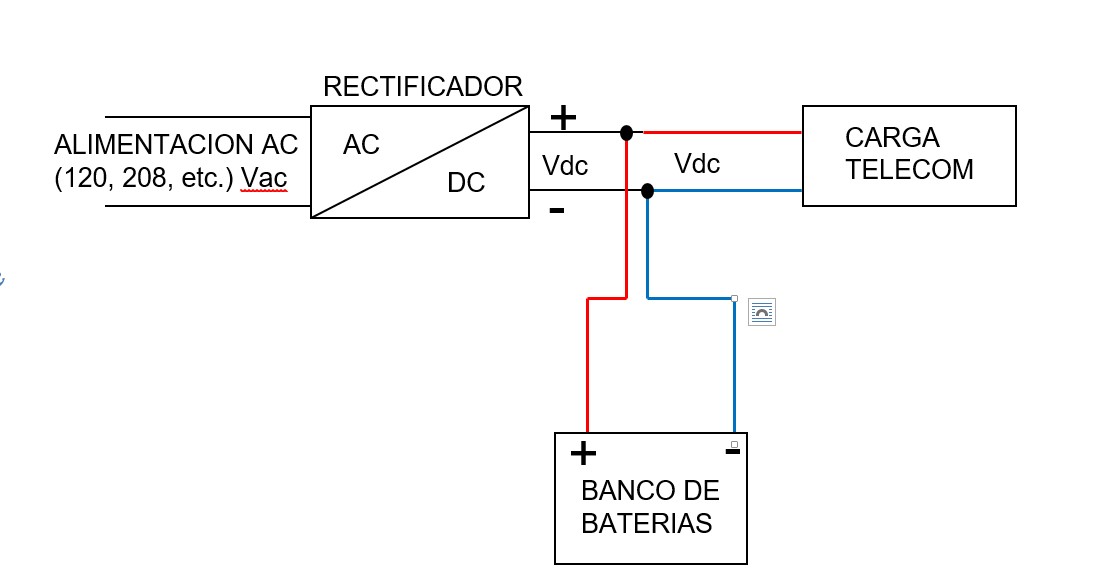
In this way, when the rectifiers are turned off due to a fault, then the batteries instantly provide the DC power supply to the telecommunications equipment.
To learn a little more about them, we invite you to read the post The battery and its generalities. I assure you that it will clear up many doubts, don’t miss it!
Up to here
We will continue with this topic in our article Electrical power equipment for telecommunications. Part 3 where we will study other backup equipment such as UPS and DC/AC inverter. Wait for it!
If you want to learn how to perform the engineering calculations for design, we offer you our Course of design of power systems for telecommunications that we are developing. In the content, you’ll be able to see the entire thematic
If you liked this post or have any questions, feel free to comment. Also, we invite you to read the posts we have published in our web energydcac.
Image sources
- mtu-solutions.com
- energydcac.com
- batteryspecialties.com.au

