I will now explain the general operation of telecommunications energy equipment, which we will do in a modular fashion.
In order for you to have the basic knowledge of the essential elements of electricity in telecommunications, we suggest you read our previous publications on the subject.
These are Electrical Power: Your First Steps and Electrical Power in Telecommunications.
It is impossible to establish a division in the way of operation of the AC power system and the DC power system.
This is because both systems, comprising AC and DC electricity, are closely linked.
Therefore, in telecommunications, the existence of one without the other is inconceivable.
This is valid both in the operation of electrical equipment in emergency situations or in operation under normal conditions.
This is for ease of understanding. Likewise, for this purpose, technicalities are reduced to a minimum.
High voltage connection
Also called «commercial AC power supply», it consists of AC power, in high voltage that comes from the distribution substation, thus being the first element of the electrical part of the telecommunications infrastructure.
A point to highlight is that, depending on the strategic importance of the building, this connection can have a double bus AC energization.
It can even come from two different electrical substations. This configuration is called «redundant power supply», which increases the operational availability of electrical equipment.
The wiring of this connection reaches the metering panel from where the AC electricity is delivered to the building’s own transformers.

It comes with 3 phases plus neutral, the ground connection is usually connected to the grounding system of the structure.
This is because, in telecommunication systems, grounding plays a fundamental role.
This is explained in the post we are preparing called Grounding systems for telecommunications. Don’t miss it!
Transformers
The telephone exchanges, for safety and service uninterruptibility reasons, have their own dedicated transformer equipment.
They reduce the voltage levels of the high voltage supply to other low voltage AC levels to be used by the telecommunications infrastructure equipment.
The transformers energize the different electrical panels in AC under normal operating conditions.
That is, if the service connection has no problems, all the panels obtain AC power from the transformers.
AC main and distribution panels
The conductors coming out of the transformers go to a main switchboard, from where they are routed to two main distribution switchboards.
One of them is called «Normal service panel» to which non-priority loads are connected.
As an example of some of them we have lighting of general areas, office equipment, kitchen and dining room and others.
The other panel is called «Emergency panel», which energizes critical loads of the telecommunications infrastructure.
Here we refer to equipment associated with the AC and DC power system such as rectifiers, UPS, among others, essential to maintain the service.

This board is backed up by the generator set, which supplies AC power when there is some kind of failure in the AC power supply.
Of the generator set or motorgenerator we will return to talk in the post electrical power equipment for telecommunications. Part 2 which is in the process of writing.
It is noteworthy that, in designs well made, the boards with AC power backup are divided by the type of equipment to which they give power supply.
So you have AC boards rectifiers, UPS, air conditioning equipment.
In the course of design of dc power systems for telecommunications we will teach you the criteria and best practices to follow in this regard. To familiarize yourself with its content, click here.
Rectifier equipment
This equipment can be considered as one of the cornerstones of the telecommunications power system.
They are energized in AC through the emergency distribution boards and convert this energy into DC electricity.
They provide power supply to electrical equipment of the telecommunications system that operate with DC and equipment that feed AC equipment from DC such as inverters and UPS of which we will talk about in this post.
Of the latter we will tell you about in the post electrical power equipment for telecommunications. Part 3.
There are equipments with various rectification technologies, the priority being their size reduction and a higher purity in the output signal.
We will talk in more detail about these equipments in the post AC – DC rectifier equipment in telecommunications that we are creating for you.
The power supply system for telecommunications, in its AC and DC power part would operate under normal conditions according to the following scheme.
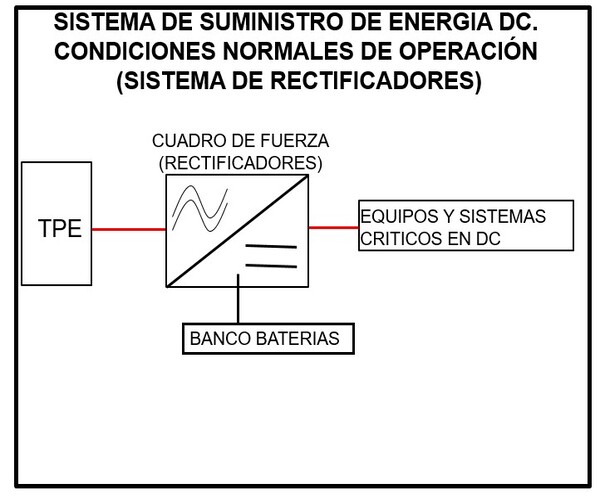
It should be noted that, in this condition, the rectifier equipment acts as a battery charger.
We will continue with this topic in the next article entitled electrical telecommunications power equipment. Part 2.
In it we will continue to discuss how each part of the power system associated with the equipment and backup elements works.
If you liked this article, or if you did not like it, let us know in the comments. We also invite you to visit our website energydcac that offers the best content on this topic and others that are sure to interest you.
Image sources
- primeraeng.com
- telecomreview.com
- energydcac.com

