AC/DC Power
Electric power: just what you need to know
The effects of electric power are probably the phenomenon best known to all, however, very few can define it and even fewer really know its parameters.
For example, did you know how electrical energy is generated, if you touch a single wire nothing happens, what is meant by phase, neutral and ground wires? These and many other questions will be clarified below in a very simple way.
It is important to note that this post is not intended to be a technical article, but we will present everything you need to know, from a user’s point of view.
But first… What is electricity?

Put as simply as possible, electrical energy is a phenomenon that circulates through the wires and plugs that make equipment work. In fact, it is present in almost everything related to everyday life.
When a fault occurs that causes a power outage, you may find that life becomes very uncomfortable.
How electricity is generated and how it reaches us

We clarify that the generation of electricity is through large alternators, whose principle of operation is the same as your car, which have large blades that can be moved by water, air, steam, etc.
Regarding solar electricity, this is produced by the photovoltaic effect of certain materials that make up the so-called solar panels.
If you want to know more about this type of renewable energy, we invite you to read our post Solar panels: what you should know before buying.
Generally, the generation of electrical energy occurs far away from our homes and is carried by cables called «high-voltage lines». To make it usable in our homes, this voltage is reduced by step-down transformers.
Finally, it reaches us through the so-called «power distribution lines». This is called the «power grid«.
How does the electric company charge us for electric service?
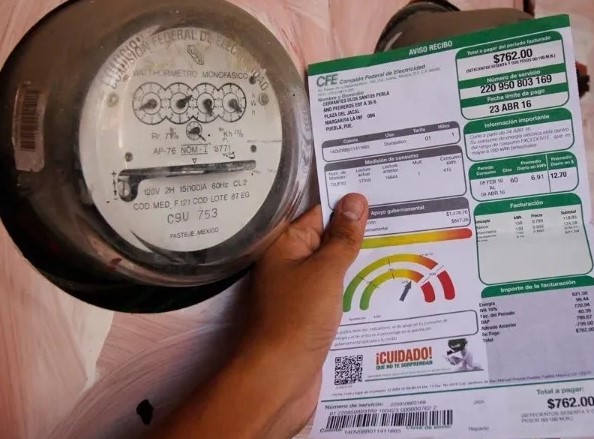

Charging is done through so-called «energy consumption meters» which determine the amount of energy you consume. This last factor is measured in the form of kilowatt hours or kWh.
In simple terms, what the company does is to determine the amount of watts you consume in an hour, divides it by 1000 and charges you the result of that division. Obviously the process is done in an automated way by the meter.
Estimating energy consumption in kWh

One way to estimate your energy consumption is to check the data on the equipment label and multiply it by the number of hours. For example, if your dishwasher says it consumes 200 W, and you use it about 3 hours a day, then its energy consumption per day will be:
CD = 200 W X 3 h = 600 Wh
Now, in most countries, the charging periods of electricity companies are 30 days, then:
CM = 600 Wh x 30 = 18000 Wh
Which in kWh would be this amount between 1000, then the monthly electrical energy consumption of your dishwasher will be 18 kWh.
You do this with each equipment and at the end you add them all up. In the electricity bills you will find out the cost per kWh, then just multiply it by the result of your consumption and you will have an idea of your monthly electricity cost.
This value can be quite onerous depending on the electricity tariff of the company that serves you, which is why energy efficiency in equipment is so important.
Cables and conductors

Usually these terms are used as synonyms, however, we believe it is important for you to know their difference, especially when buying them.
Cables are conductors that have a coating or insulation, which comes in different types and colors depending on the use and other factors.
The name of this coating depends on each country. Another important parameter refers to the conductor gauge, in this respect most countries have standardized this variable using its area in mm2.
Therefore, when purchasing a wiring you must specify its gauge and type of insulation, which depend on the amount of current that will circulate through them, the conduits that will contain them, voltage levels and others.
Types of electrical energy
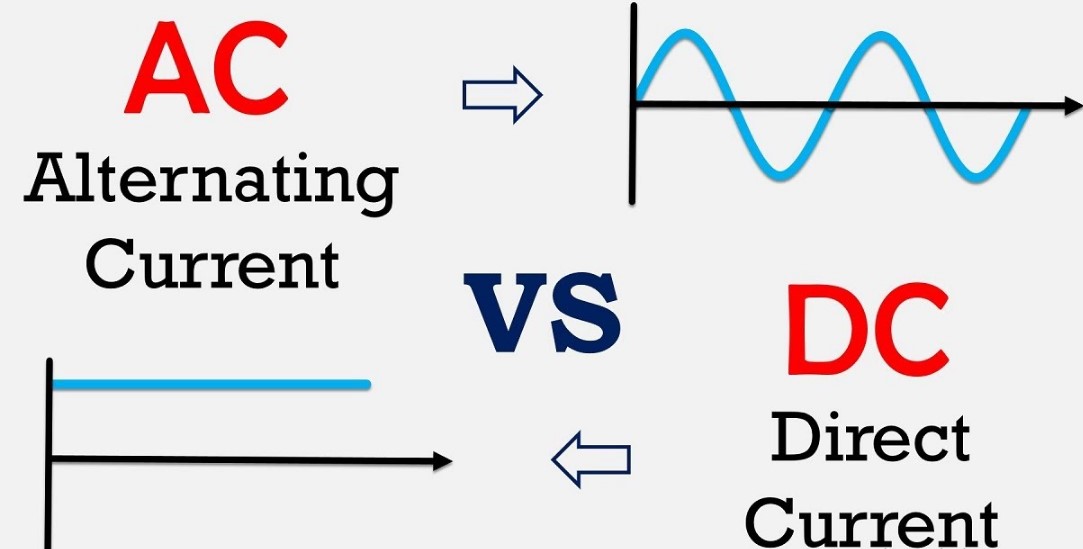
Regardless of the energy source, there are only 2 types of electrical energy which are continuous or DC and alternating or AC.
Both have big differences, for example, in the alternating electricity there are the phase conductors that carry the energy and the neutral that establishes a path for the balance of the currents.
In the case of direct electricity, there are only 2 conductors through which the current circulates.
Now, as far as electrical safety is concerned, both have in common that if you touch only one wire there is no problem, but if you touch both, you will receive an electric shock.
However, it is not recommended that you take this risk. Let’s say you are in contact with a conductor in alternating energy, but if you accidentally touch a fixed metal object or do not have insulating footwear, you will most likely suffer an electrical accident.
In view of the above, it is better to leave this activity to the experts and do not take unnecessary risks.
In our content we are preparing called Electrical energy in telecommunications. Part 1 and Electrical energy in telecommunications. Part 2, we explain everything you need to know about both kinds of electricity.
This in a very simple way and without technicalities. By subscribing to energydcac you will find out about our latest news and contents, sign up now!

