Sistemas de Energía DC/AC
Open lead-acid stationary battery
The open lead-acid stationary battery is the most widely used as a backup for DC power systems. It’s prevalent in various industries and strategic sectors like telecommunications, where continuous service is essential.
This popularity is attributed to their high electrochemical performance, extended lifespan, and cost-effectiveness within their domain. Moreover, they are deep-cycle batteries.
They hold a substantial presence in the market, and it’s precisely this high demand and supply that makes them more affordable.
To help you get a better context, we suggest reading our article Batteries and their fundamentals. Similarly, we recommend exploring the content about Stationary batteries and their types.
Within this technology, the most commonly used types are open or vented batteries and sealed or valve-regulated batteries. Next, we will provide a brief description of each. Let’s get started!
Open lead-acid stationary battery
Also known as a «vented battery.» It is characterized by having exposed and accessible liquid electrolyte. It allows for the addition of distilled water to maintain electrolyte levels and extend lifespan.
Next, we present a typical battery cell with its components and key features.

We should also point out that in high-capacity batteries (greater than 700 Ah), their terminals can consist of two or three posts per pole.
This is due to the substantial amount of energy they can store and release. The configuration provides the advantage of being a deep-cycle battery.
The distinctive component of the open lead-acid stationary battery: the liquid electrolyte
The crucial parameter of this element is specific gravity or density. It measures the weight or density of the electrolyte in relation to the water it contains. Its units are kg/m3 or g/L, and commonly used values are around 1220 and 1240.
This density is directly related to the battery’s state of charge, as explained in our upcoming post titled Determining the state of a stationary battery. We invite you to read it for further insight.
How temperature affects the electrolyte density in open stationary batteries
As the temperature of the electrolyte increases, its volume also expands while keeping the mass constant. This results in a decrease in density under these conditions.
That’s why when taking density readings, it’s important to record the temperature as well to ensure their accuracy. Subsequently, to obtain the actual value, you should apply the temperature correction table provided by the manufacturer.
Connection of the open lead-acid stationary battery
By this, we are referring to the types of charging that these batteries must undergo to maintain their functionality. Similarly, it aims to extend their lifespan and ensure they can serve as continuous-service batteries.
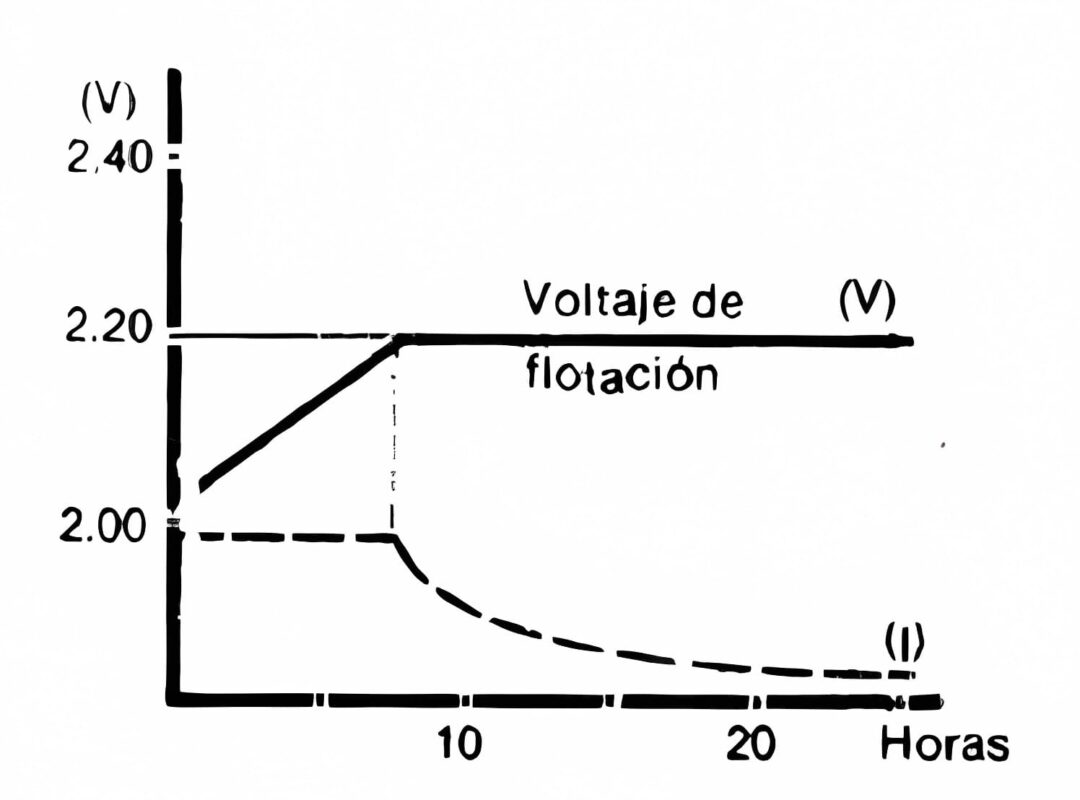
Float Charging
The purpose of float charging is to compensate for the internal self-discharge of the battery and counteract its internal consumption.
For open lead-acid batteries, the appropriate voltage level per cell is around 2.20 Vdc. To achieve this, a form of float charging with current limitation is used, and its behavior is illustrated below.
Equalization Charging
With this mode, a higher amount of energy is supplied to the batteries in order to charge them quickly. This is achieved by increasing gasification to make the electrolyte move and homogenize.
Another benefit is voltage equalization across all cells. This ensures that they maintain uniform characteristics, thus extending their lifespan.
The equalization voltage for open lead-acid batteries is around 2.3 Vdc per cell. Below is a graph depicting the charging process of a battery using a charger set to this configuration.
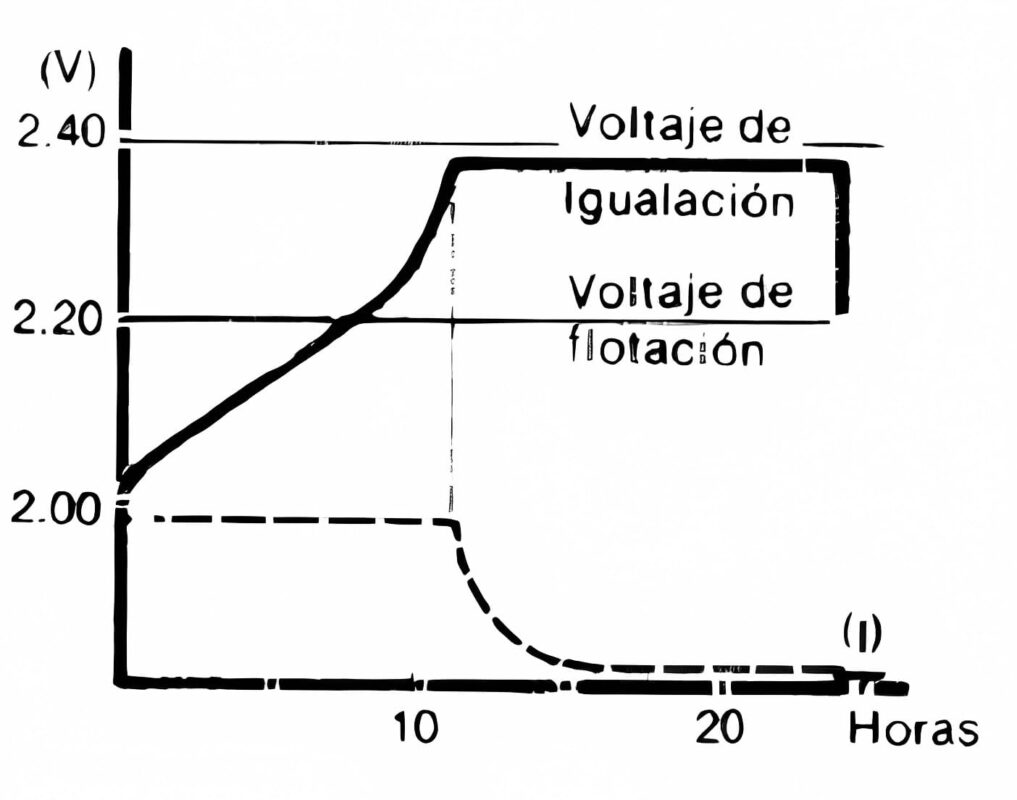
However, it’s important to note that this charging process should have a limit, usually around 20 hours. This limitation is in place because over time, it can lead to temperature rise that might cause irreversible damage.
Additionally, it can result in a reduction of the electrolyte’s water content, so you need to be attentive to compensating for it.
Here we conclude
In our upcoming post Sealed lead-acid valve regulated stationary battery, you will discover its attributes. Read it as you’re sure to find it appealing!
Likewise, we have a Sizing and design of dc power systems for telecommunications course tailored for you. With it, you’ll learn how to plan and determine the batteries to use according to your needs. Follow this link to explore its content.
Before we bid farewell, we also invite you to visit the energydcac blog, where you’ll find plenty of engaging content.
Video to learn more about open lead-acid stationary batteries
Image sources
- energydcac.com
- ecofener.com

