AC/DC Power
Voltage measurement in stationary battery discharge test
The stationary battery discharge test is one of the tests that provides the most reliable results regarding the operational status of these banks. In this post, we will present the way to analyze and interpret the battery voltage measurement, obtained.
The execution method is explained in our post on Stationary battery discharge test. Be sure to read it!
You should know that this test is applicable to all types of stationary batteries, whether open-ventilated or sealed with regulated valves.
However, its effectiveness depends on the correct interpretation of the measurements obtained. For this purpose, here is a brief but concise guide regarding the measured battery voltage values. Let’s get started!
Voltage levels
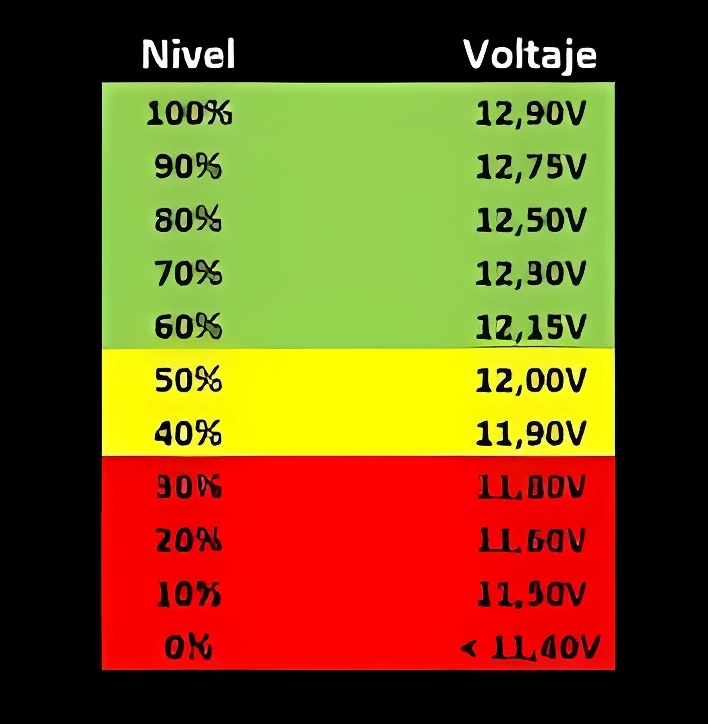
When disconnecting the bank from its normal load and the rectifiers, it remains in “open circuit” or “idle.” In these conditions, the voltage in each of the cells is between 2.0 and 2.1 Vdc. In the case of 12 Vdc blocks, this value should be between 12 and 12.6 Vdc.
If any of the cells is outside of this range. We suggest not conducting the test and applying an equalization voltage charge to ensure voltage levels are as uniform as possible.
If the voltages continue to be out of range, it is recommended not to proceed with the test until the abnormal elements are replaced.
Now, concerning the voltages measured during the test, they should remain consistent across all cells over time. If any cell shows a difference of more than 10% compared to the maximum and minimum readings of the others, you should closely monitor that particular element.
This is because it indicates damage and compromises the operation of the entire battery bank.
Below, you will find a table displaying voltage measurements obtained during the first 20 minutes of a test.
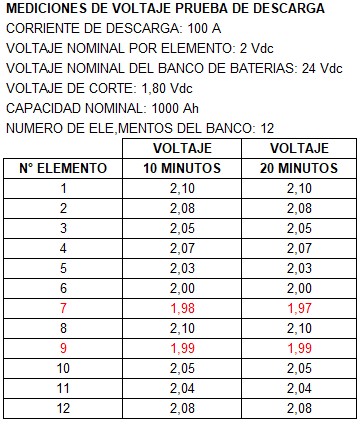
Keep in mind that this is just a small part of the test. According to the procedure outlined in The battery discharge test: What does it consist of and what is it used for?. The test’s duration can span several hours depending on the conditions of the bank.
Analysis of Voltage Measurement Readings
From the data obtained earlier, the following can be inferred:
Most of the elements are in condition to continue the test, except for cells 7 and 9. These cells have low voltage and a tendency to rapidly reduce voltage.
This is reiterated because their voltage level is within 10% lower than the cell with the lowest voltage.
Due to this situation, it is recommended to suspend the test and replace cells 7 and 9. After replacement, the test should be repeated to verify the health of the batteries.
Now, if there were no issues with the damaged cells, you could continue with the protocol. Just make sure that the voltage reduction occurs according to the manufacturer’s catalog.
This aspect is explained in our article “Discharge Tables from the Battery Manufacturer’s Catalog.” Be sure to read it as it will be very instructive!
As you can see, the parameter of each battery element is of great importance. Since it is one of the variables with the greatest influence in defining their health.
To learn more about these devices, we invite you to read our content on energydcac. It will undoubtedly be very useful, and we also present articles on other interesting topics related to electrical energy in its various types and applications.
We also offer the Sizing and designing dc power systems for telecommunications and critical systems course . In this course, you will thoroughly learn about using batteries as backup for equipment. You can see all the topics covered in the mentioned course by clicking here.
We are at your disposal to clarify any doubts that may arise.
Image source
- bateriasyamperios.com
- energydcac.com


Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.